ASAL Humanitarian Network (AHN)
ASAL Humanitarian Network – Drought Response Baseline
Baseline Assessment Highlights Food Insecurity and Livelihood Vulnerability in Mandera County
Baseline Assessment – January 2022
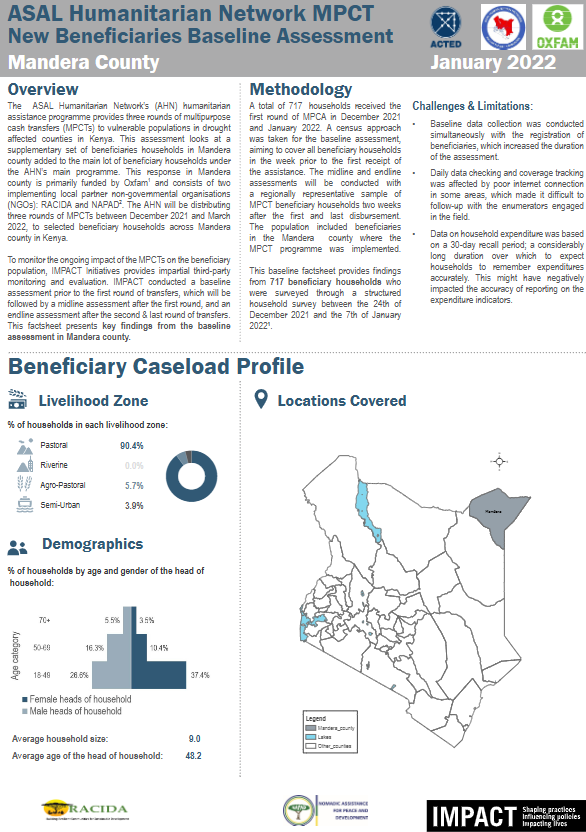
The ASAL Humanitarian Network (AHN) conducted a baseline assessment in Mandera County to understand the pre-intervention conditions of households targeted under its multi-purpose cash transfer (MPCT) drought response. The initiative, funded by Oxfam and implemented by Rural Agency for Community Development and Assistance (RACIDA) and Nomadic Assistance for Peace and Development (NAPAD), aimed to support the most drought-affected households through three cash transfer rounds between December 2021 and March 2022.
Findings from the IMPACT Initiatives assessment indicate widespread food insecurity and low household resilience:
Food Consumption Score (FCS): 62.6% of households had poor FCS, and only 17% achieved acceptable consumption.
Household Dietary Diversity Score (HDDS): 87.2% of households had low dietary diversity.
Average monthly income: KES 4,095, with 38% of household expenditure spent on food.
Reduced Coping Strategy Index (rCSI): 21.5, showing heavy reliance on negative coping mechanisms such as reducing meal frequency and portion size.
The majority of households (97.3%) reported that their communities were affected by drought, with 95.7% citing rangeland losses and 43% reporting inter-community conflict linked to resource scarcity. Livelihoods were predominantly pastoral (90%), with casual labour (44%) and begging (19%) as the main income sources.
Protection and accountability indicators were positive: 100% of respondents felt safe during registration, and 99.7% confirmed no payments were made for inclusion. 65% of households reported being consulted by NGOs about their needs, reflecting early adherence to participatory and locally led humanitarian principles.
The baseline underscores the urgency of cash-based early action in Mandera’s pastoral zones to improve food access, support coping capacities, and mitigate drought-induced vulnerability.